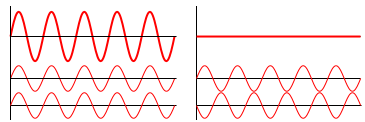
In physics, interference is the process in which two or more light, sound, or electromagnetic waves of the same frequency combine to reinforce or cancel each other, the amplitude of the resulting wave being equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the combining waves. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves or matter waves. One of the best examples of interference is demonstrated by the light reflected from a film of oil floating on water. Another example is the thin film of a soap bubble, which reflects a spectrum of beautiful colors when illuminated by natural or artificial light sources.
- المعلم: أ.د. محمد على محمد صيام

