
Course content/• Definition and classification. Stereoisomers of (+) glucose. Oxidation and effect of alkali.
• Ozazone. Epimers. Lengthening and shortening the carbon chain of aldoses.
• Configuration of (+) glucose. Fisher proof. Optical families.
• Cyclic structure of D(+) glucose. Methylation, glucosides. Determination of ring size. Conformation.
• Disaccharides: Proof of structure and properties
• Polysaccharides: starch and cellulose structure, properties .
• Some applications on different saccharides. Problems.
• Structure and isoelectric point of amino acids.
• Preparation and reactions of amino acids.
• Geometry of the peptide linkage. Terminal residue analysis. Determination of structure and preparation of peptides.
• Proteins: classification, str…
Course Description: -
This course deals with the chemistry of fats, lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, as biomolecules. Also it deals with the chemistry of detergents..
Course Contents: -
Biomolecules: -
1- Fats:
· Fats: fatty acids (lipids)
· Unsaturated fats
· Phosphoglycerides
· phospholipids and cell
membranes.Detergents
2-Carbohydrates; -
Structure, properties, chemical reactivity, configuration, optical properties, and applications of monosaccharides, disaccharide, and poly saccharide (starch, cellulose, and glycogen).
3- Amino Acids and Proteins: -
Molecular structure, nomenclature, properties, and chemical reactivity of amino acids, peptides, and protein
• Ozazone. Epimers. Lengthening and shortening the carbon chain of aldoses.
• Configuration of (+) glucose. Fisher proof. Optical families.
• Cyclic structure of D(+) glucose. Methylation, glucosides. Determination of ring size. Conformation.
• Disaccharides: Proof of structure and properties
• Polysaccharides: starch and cellulose structure, properties .
• Some applications on different saccharides. Problems.
• Structure and isoelectric point of amino acids.
• Preparation and reactions of amino acids.
• Geometry of the peptide linkage. Terminal residue analysis. Determination of structure and preparation of peptides.
• Proteins: classification, str…
Course Description: -
This course deals with the chemistry of fats, lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, as biomolecules. Also it deals with the chemistry of detergents..
Course Contents: -
Biomolecules: -
1- Fats:
· Fats: fatty acids (lipids)
· Unsaturated fats
· Phosphoglycerides
· phospholipids and cell
membranes.Detergents
2-Carbohydrates; -
Structure, properties, chemical reactivity, configuration, optical properties, and applications of monosaccharides, disaccharide, and poly saccharide (starch, cellulose, and glycogen).
3- Amino Acids and Proteins: -
Molecular structure, nomenclature, properties, and chemical reactivity of amino acids, peptides, and protein
- Teacher: تحية بيومى مصطفى بوالخير .
- Teacher: رضوى احمد السيد مصطفى .
- Teacher: شادية محمد قدرى .
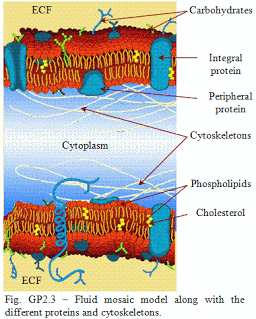
The students should study the animal cell,how the structure of specialized animal cells suit their different functions. Also, students should study the structure and physiological function of cell membrane and different cellular organelles.
- Teacher: أسماء مجدي أحمد زعزع .
- Teacher: سميحة محمد عبد الدايم زايد .
- Teacher: فاطمة مختار على فوده .
- Teacher: هبه السيد عبدالعاطى اسماعيل احمد .

