
التفكير العلمي يطلق عليه العلماء هذا المسمى لأنهم ملتزمون في استقصاءاتهم العلمية يسعون لفهم الظواهر الطبيعية وتفسيرها والتنبؤ بها مع اختلاف مناهجهم العلمية في البحث والاستقصاء إلا أن سلوكهم الفكري يتميز بأعلى درجة من الموضوعية والضبط والتسلسل المنطقي المنظم القائم على الدليل والبرهان فالتفكير العلمي ليس تفكيرا متخصصا بموضوع ما؛ بل يمكن ان يوجه في معالجه جميع الموضوعات و القضايا التي تواجهنا. و يعد التفكير العلمي ضرورة للفكر و طريقة الى الابداع في شتى مجالات العلم و المعرفة. للتفكير العلمي مهارات تستحق الدراسة والتطبيق العملي وخطوات يتم التعرف عليها بمنهجيه علميه و هذا ما سوف يتم التعرف عليه و دراسته في هذا المقرر.
- Enseignant: رشا عبد النبي عبد الحميد علي .
- Enseignant: هيام عادل عبد العظيم .
- Enseignant: رشا عبد النبي عبد الحميد علي .
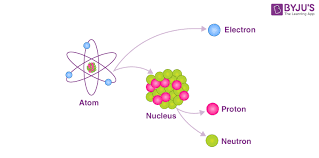
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change.
The term atomic physics can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of atomic and nuclear in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei.
As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the wider context of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Physics research groups are usually so classified.. For example, the fact that each element has its own characteristic “fingerprint” spectrum has contributed significantly to advances in material science and also in cosmology. The aim of this course is to guide the learner through a chronological development of Atomic Physics. The learner begins by studying the development of atomic models from Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford and finally Bohr. After atomic models the learner is guided through a phenomenon that led to the discovery of the electron and its negative charge. Gas discharge experiments also laid the ground as to how atoms
could be excited.
The term atomic physics can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of atomic and nuclear in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei.
As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the wider context of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Physics research groups are usually so classified.. For example, the fact that each element has its own characteristic “fingerprint” spectrum has contributed significantly to advances in material science and also in cosmology. The aim of this course is to guide the learner through a chronological development of Atomic Physics. The learner begins by studying the development of atomic models from Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford and finally Bohr. After atomic models the learner is guided through a phenomenon that led to the discovery of the electron and its negative charge. Gas discharge experiments also laid the ground as to how atoms
could be excited.
- Enseignant: نجلاء أحمد محمد شاهين .
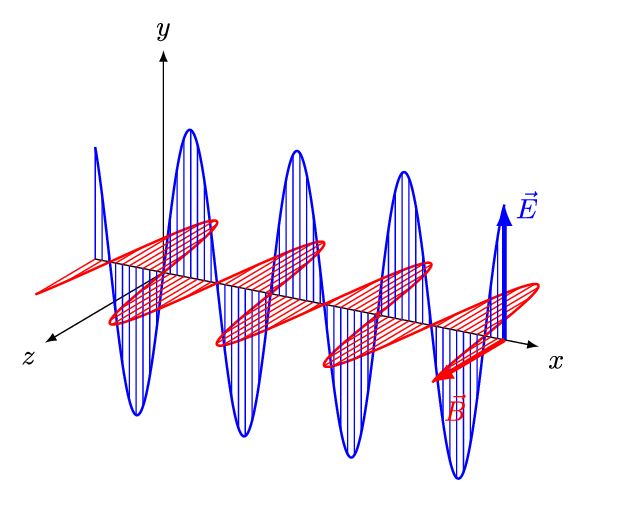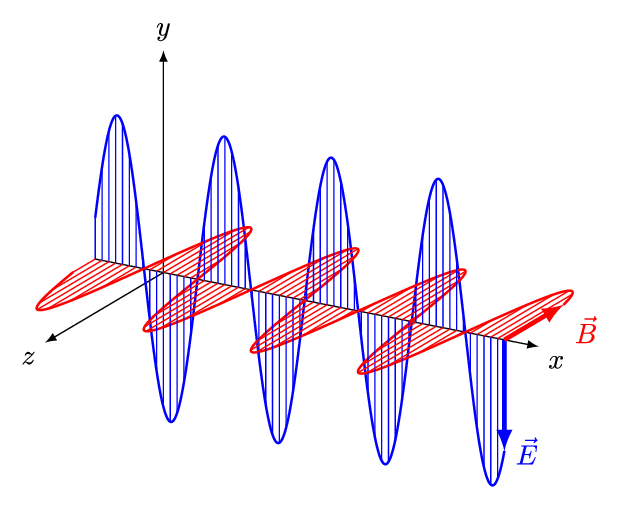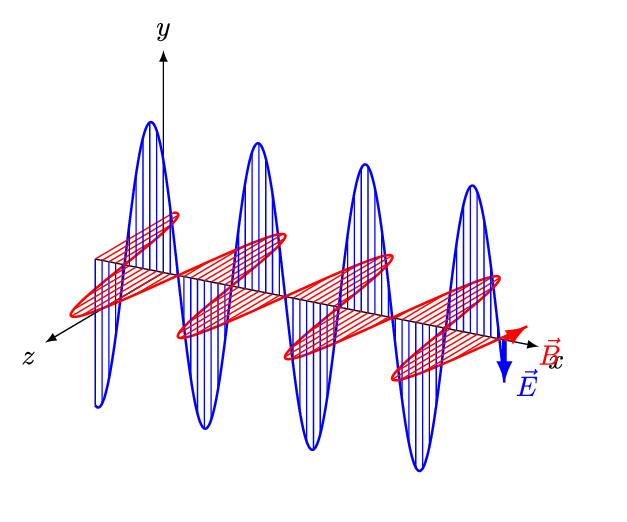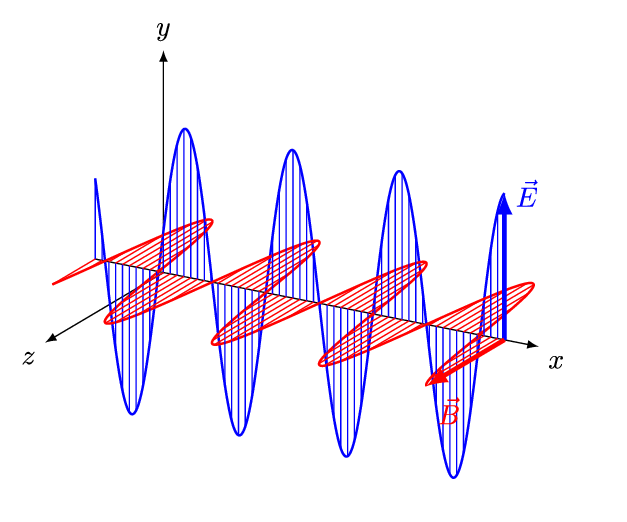
Aim of the electromagnetics course is deduce Maxwell's equations.
- Enseignant: إيمان رضا أبو اليزيد محمد .

