A- Basic Information
Title: Applications of computer programs (1) Code: HETC 283
Credit Hours: 2 hours Lecture: 1 hour
Practical: 3 hours Total: 4 hours
B- Professional Information
1 – Overall aims of course
This course is designed to make the student familiar to the computer system (hardware and software), using PC and managing files and folders, knowing computer networks and its types, and also give student basic information about computer programs and how to deal with some of it such as (Word Processing: Microsoft Word).
2 – Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1- Illustrate Computer system and its components.
a2- Show understanding of the difference between Computer Hardware and Software.
a3- Know the different input & output devices and their usage.
a4- know the commands and tasks of Microsoft word program.
b- Intellectual skills
b1- Identify the basic components of computer.
b2- Apply the skills in making neat word document.
c- Professional and practical skills
C1- The ability of dealing with Microsoft word program.
C2- The ability to surf the Internet.
d- General and transferable skills
d1-Use MS-Windows.
d2-Use MS-Office (Word).
d3-Use the Internet.
Title: Applications of computer programs (1) Code: HETC 283
Credit Hours: 2 hours Lecture: 1 hour
Practical: 3 hours Total: 4 hours
B- Professional Information
1 – Overall aims of course
This course is designed to make the student familiar to the computer system (hardware and software), using PC and managing files and folders, knowing computer networks and its types, and also give student basic information about computer programs and how to deal with some of it such as (Word Processing: Microsoft Word).
2 – Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1- Illustrate Computer system and its components.
a2- Show understanding of the difference between Computer Hardware and Software.
a3- Know the different input & output devices and their usage.
a4- know the commands and tasks of Microsoft word program.
b- Intellectual skills
b1- Identify the basic components of computer.
b2- Apply the skills in making neat word document.
c- Professional and practical skills
C1- The ability of dealing with Microsoft word program.
C2- The ability to surf the Internet.
d- General and transferable skills
d1-Use MS-Windows.
d2-Use MS-Office (Word).
d3-Use the Internet.
- Enseignant: أيه عبد الرحمن عبدالحليم جاد .
- Enseignant: ايناس اشرف احمد العقده .
- Enseignant: سهير محمد عبد الخالق عرفه .
1. Dimensions and Physical units.
2. Vectors.
3. Static and dynamic of solid bodies.
4. Elasticity.
5. Viscosity.
6. Surface tension.
7. Concept of heat.
8. Thermometers.
9. Heat expansion.
10. Heat capacity.
11. Specific heat.
12. Transfer of heat.
13. Radiation and its application.
14. Law of gases.
15. First law of thermodynamic.
16.Second law of thermodynamic.
2. Vectors.
3. Static and dynamic of solid bodies.
4. Elasticity.
5. Viscosity.
6. Surface tension.
7. Concept of heat.
8. Thermometers.
9. Heat expansion.
10. Heat capacity.
11. Specific heat.
12. Transfer of heat.
13. Radiation and its application.
14. Law of gases.
15. First law of thermodynamic.
16.Second law of thermodynamic.
- Enseignant: سمر عادل محمد عبد الغفار .
- Enseignant: هيام عبد العزيز على الزاهد .

B- Professional Information
1 – Overall aims of course
The course aim to develop the information technology about different fibers used in textile production and how convert different textile fibers to yarn by using different techniques of spinning processes and then how convert yarn to fabrics.
The syllabus aims to help learners to.
Define the characteristics of textile fibers and its classification.
Technology knowledge development about spinning machines using to producing different yarns.
Knowledge about converting fibers into yarns technically.
Introduction knowledge about how to convert yarns to fabrics
Developing the student's cognitive skill about the physical and mechanical properties of different fibers.
Knowledge about the yarn properties and define the factors effects on these properties.
Knowledge about preparatory processes of weaves and defines the main basic woven structures.
-----------------------------
2 –Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1-define meaning of textile fibers.
a2- recognize classification of textile fibers.
a3- identify the various properties of different fibers.
a4-outlineTechnical knowledge about converting fibers into yarns.
a5- recognizes the most important factors effects on yarn properties.
a6- describe the preparatory processes of spinning cotton yarn.
a7- explain how to produce cotton yarn.
a8- clarify the spinning process.
a9- explain how to produce wool yarn.
a10- explain how to produce silk yarn.
a11- explain how to produce man-made yarn.
a12- identify types of yarns and its classification.
a13-Identify yarn count and how can calculate it.
a14- describe preparatory processes of weaving.
a15- explain how to produce viscose rayon fiber.
a16- identify the types of chemical spinning.
b- Intellectual skills
b1-classify the different types of textile fibers.
b2- discuss any type of textile fibers classification.
b3- compare between natural and manmade fibers.
b4-Compare between plants and animal fibers.
b5- compare different properties for different fibers.
b6- explains the different spinning types of different textile fibers.
b7- Discuss basic principles of the spinning.
b8- Discuss any process of reparatory spinning processes of cotton yarn.
b9- Demonstrate relation between the yarn size and its count.
b10- Distinguish yarn count of different types of threads.
b11- Classify different types of yarns.
b12- select different threads for suitable applications according to their characteristics.
B13- compare between main basic woven structures.
B14- discuss the preliminary processes of woven.
B15- compare between three types of chemical spinning.
B16- discuss the viscose process.
c- Professional and practical skills
C1- detect about new types in textile fibers sector.
C2- explains about different properties for different fibers.
C3- detect about new technical trends in spinning textile fibers sector.
C4- explains about different types of yarns and different using of it.
C5- solves the problems to calculate yarn count of different threads.
C6- explains about preparatory processes of woven and the basic woven structures.
d- General and transferable skills
D1- suggests new textile fibers and how to convert yarns.
D2-collect information or a new trend about any topics related to textile technology.
1 – Overall aims of course
The course aim to develop the information technology about different fibers used in textile production and how convert different textile fibers to yarn by using different techniques of spinning processes and then how convert yarn to fabrics.
The syllabus aims to help learners to.
Define the characteristics of textile fibers and its classification.
Technology knowledge development about spinning machines using to producing different yarns.
Knowledge about converting fibers into yarns technically.
Introduction knowledge about how to convert yarns to fabrics
Developing the student's cognitive skill about the physical and mechanical properties of different fibers.
Knowledge about the yarn properties and define the factors effects on these properties.
Knowledge about preparatory processes of weaves and defines the main basic woven structures.
-----------------------------
2 –Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1-define meaning of textile fibers.
a2- recognize classification of textile fibers.
a3- identify the various properties of different fibers.
a4-outlineTechnical knowledge about converting fibers into yarns.
a5- recognizes the most important factors effects on yarn properties.
a6- describe the preparatory processes of spinning cotton yarn.
a7- explain how to produce cotton yarn.
a8- clarify the spinning process.
a9- explain how to produce wool yarn.
a10- explain how to produce silk yarn.
a11- explain how to produce man-made yarn.
a12- identify types of yarns and its classification.
a13-Identify yarn count and how can calculate it.
a14- describe preparatory processes of weaving.
a15- explain how to produce viscose rayon fiber.
a16- identify the types of chemical spinning.
b- Intellectual skills
b1-classify the different types of textile fibers.
b2- discuss any type of textile fibers classification.
b3- compare between natural and manmade fibers.
b4-Compare between plants and animal fibers.
b5- compare different properties for different fibers.
b6- explains the different spinning types of different textile fibers.
b7- Discuss basic principles of the spinning.
b8- Discuss any process of reparatory spinning processes of cotton yarn.
b9- Demonstrate relation between the yarn size and its count.
b10- Distinguish yarn count of different types of threads.
b11- Classify different types of yarns.
b12- select different threads for suitable applications according to their characteristics.
B13- compare between main basic woven structures.
B14- discuss the preliminary processes of woven.
B15- compare between three types of chemical spinning.
B16- discuss the viscose process.
c- Professional and practical skills
C1- detect about new types in textile fibers sector.
C2- explains about different properties for different fibers.
C3- detect about new technical trends in spinning textile fibers sector.
C4- explains about different types of yarns and different using of it.
C5- solves the problems to calculate yarn count of different threads.
C6- explains about preparatory processes of woven and the basic woven structures.
d- General and transferable skills
D1- suggests new textile fibers and how to convert yarns.
D2-collect information or a new trend about any topics related to textile technology.
- Enseignant: إيناس محمد عبد الفتاح .
- Enseignant: هبة زكريا محمد أبو حشيش .
This course gives students the basic knowledge of textile chemistry. It deals with the properties of textile fibers; physical, chemical in addition to the serviceability properties. Also it explains the classification of textile fibers according to their source. This course allows student to recognize the natural fibers (cotton, flax, wool and silk) and regenerated fibers ( viscose, acetate and lyocell). It explains the chemical and physical structure of each fiber, their production steps, the properties and the end uses of each fibers.
- Enseignant: رحاب محمود قطب على .
- Enseignant: نجلاء عبد العظيم أمين السيد .
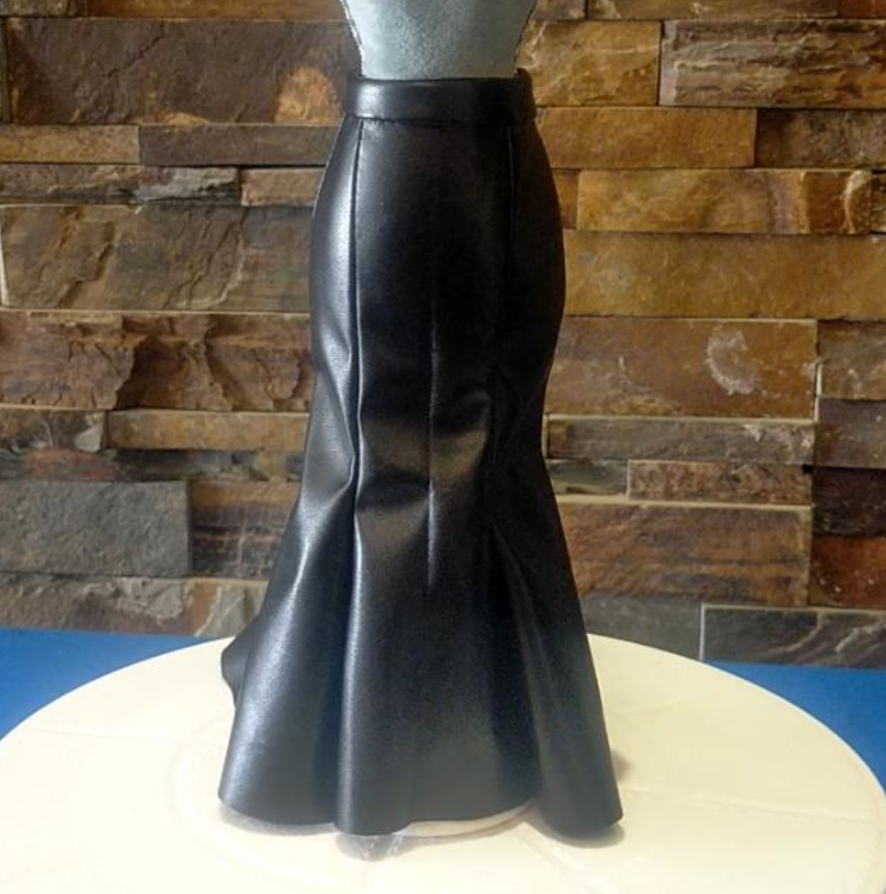

1 – Overall aims of course
This course develops and extends the range of skills making drafts and paper patterns, their layout, methods of flat pattern making for skirts, and trousers and their variations. These concepts have to be applied in the creation of fashion ensembles.
Students will learn advanced pattern making with multiple variations of the basic blocks. Students will learn the technique of style reading and developing patterns for skirts and trousers. Students will be further enriched with the experience of making commercial paper patterns and grading patterns for skirts and trousers pattern.
2 – Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1- Define the terms used when drafting basic women's skirt patterns such as block, panel skirt, vent and box pleated, inverted pleated, kilt skirt, and etc.
a2 - Define the terms used when drafting basic women's pants patterns such as block, body rise, trousers with pleated waist line, flared and gathered trousers and etc.
a3- List the measurements required to draft the basic pattern for women's skirt, pants.
A4- List Basic principles of drafting patterns on paper and testing them in muslin on three-dimensional forms for women's skirts and pants.
A5- Define the grain line and
b- Intellectual skills
b1- Differentiate between the flat blocks and the form blocks.
b2- choosing between the different types of skirt's waist bands, which is suitable with the style
b3- Differentiate between women's figure type.
b4 Choosing the best style for each figure type
c- Professional and practical skills
1c- Create the appropriate pattern and pattern alteration for women's skirts suitable for each design using standard or personal measurements.
2c- Modify the pattern to meet the aimed design.
3c-Estimate the appropriate materials used for skirts and trousers.
4c- Select the best finishing technique could be used in each model or Design.
5c- Evaluate the final product from design, material, fit, and finishing techniques.
6c- Design the final personal project with suitable pattern, material, finishing technique, facing, and interfacing.
d- General and transferable skills
d1- Set tasks and manage their time and jobs as well as acquire self and long-life learning.
d2- Use new technological available tools, informant & communication technology.
This course develops and extends the range of skills making drafts and paper patterns, their layout, methods of flat pattern making for skirts, and trousers and their variations. These concepts have to be applied in the creation of fashion ensembles.
Students will learn advanced pattern making with multiple variations of the basic blocks. Students will learn the technique of style reading and developing patterns for skirts and trousers. Students will be further enriched with the experience of making commercial paper patterns and grading patterns for skirts and trousers pattern.
2 – Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
a- Knowledge and understanding:
a1- Define the terms used when drafting basic women's skirt patterns such as block, panel skirt, vent and box pleated, inverted pleated, kilt skirt, and etc.
a2 - Define the terms used when drafting basic women's pants patterns such as block, body rise, trousers with pleated waist line, flared and gathered trousers and etc.
a3- List the measurements required to draft the basic pattern for women's skirt, pants.
A4- List Basic principles of drafting patterns on paper and testing them in muslin on three-dimensional forms for women's skirts and pants.
A5- Define the grain line and
b- Intellectual skills
b1- Differentiate between the flat blocks and the form blocks.
b2- choosing between the different types of skirt's waist bands, which is suitable with the style
b3- Differentiate between women's figure type.
b4 Choosing the best style for each figure type
c- Professional and practical skills
1c- Create the appropriate pattern and pattern alteration for women's skirts suitable for each design using standard or personal measurements.
2c- Modify the pattern to meet the aimed design.
3c-Estimate the appropriate materials used for skirts and trousers.
4c- Select the best finishing technique could be used in each model or Design.
5c- Evaluate the final product from design, material, fit, and finishing techniques.
6c- Design the final personal project with suitable pattern, material, finishing technique, facing, and interfacing.
d- General and transferable skills
d1- Set tasks and manage their time and jobs as well as acquire self and long-life learning.
d2- Use new technological available tools, informant & communication technology.
- Enseignant: خالد محمد أحمد عبده .
- Enseignant: كاميليا موسى محمد الزينى .