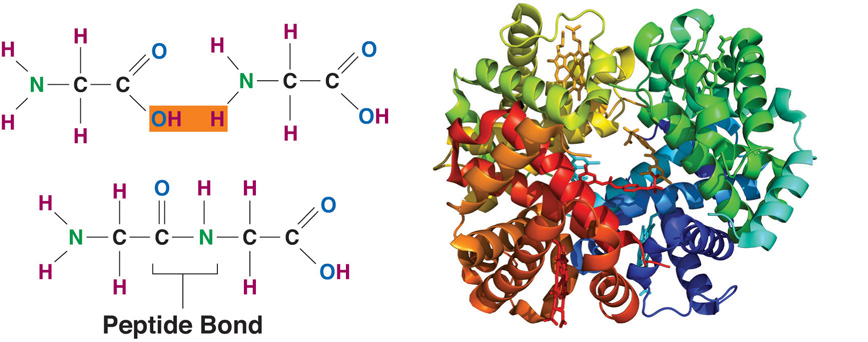
Amino acids, peptides and proteins are important constituents of food. They supply the required building blocks for protein biosynthesis. In addition, they directly contribute to the flavor of food and are precursors for aroma compounds and colors formed during thermal or enzymatic reactions in production, processing and storage of food. Other food constituents, e. g., carbohydrates, also take part in such reactions. Proteins also contribute significantly to the physical properties of food through their ability to build or stabilize gels, foams, emulsions and fibrillar structures. The nutritional energy value of proteins (17 kJ/g or 4 kcal/g) is as high as that of carbohydrates. The most important sources of protein are grain, oilseeds and legumes, followed by meat and milk. In addition to plants and animals, protein producers include algae (Chlorella, Scenedesmus, Spirulina spp.), yeasts and bacteria (single-cell proteins [SCP]).
- Teacher: Dr. ا.د. سعد رمضان محمد حسن عطالله
- Teacher: Dr. مارتينا عاطف رشيد
- Teacher: Dr. يوسف مجدي يوسف فهمي

